Choosing the right leadership style is crucial for the success and growth of any organization. Different styles of leadership can significantly impact team dynamics, employee morale, and overall organizational performance. Here’s a guide to understanding various leadership styles and determining which one best fits your organization’s needs.
1. Autocratic Leadership
1.1. Characteristics
Action: Autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally and expect employees to follow orders without input or feedback.
Benefits: This style can be effective in situations requiring quick decision-making and clear direction, especially in high-pressure environments.
Example: In a crisis or emergency situation, an autocratic leadership style might be necessary to ensure quick and decisive action.
1.2. When to Use
Action: Use autocratic leadership when tasks are highly urgent, complex, or when a clear direction is needed.
Benefits: Ensures that decisions are made swiftly and reduces confusion in fast-paced scenarios.
Example: Military operations often rely on autocratic leadership to maintain order and execute strategies efficiently.
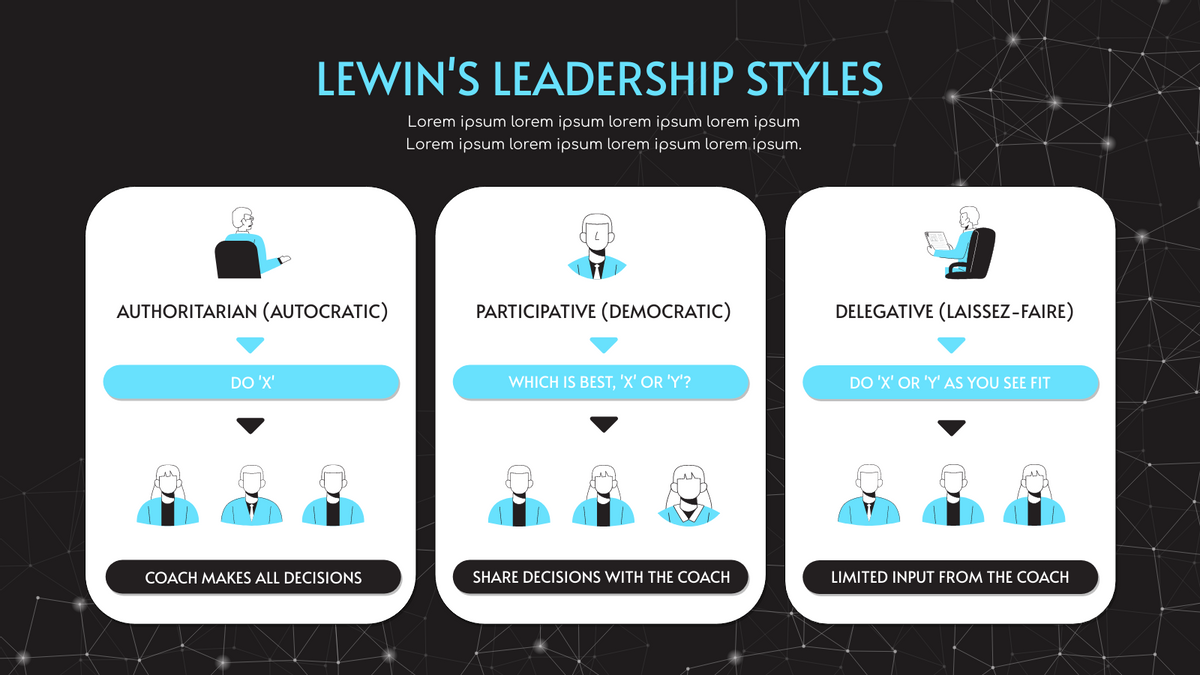
2. Democratic Leadership
2.1. Characteristics
Action: Democratic leaders involve team members in decision-making processes, valuing their input and feedback.
Benefits: This style fosters collaboration, increases employee engagement, and can lead to more creative and innovative solutions.
Example: In creative industries like advertising or tech startups, democratic leadership can harness diverse ideas and drive innovation.
2.2. When to Use
Action: Employ democratic leadership in situations where team input is valuable, and decisions benefit from collective insight.
Benefits: Enhances team morale and commitment, and improves decision quality through diverse perspectives.
Example: Product development teams often benefit from democratic leadership as it encourages team members to contribute ideas and feedback.
3. Transformational Leadership
3.1. Characteristics
Action: Transformational leaders inspire and motivate employees to exceed their own self-interests for the good of the organization.
Benefits: This style promotes high levels of engagement, creativity, and innovation by encouraging a shared vision and purpose.
Example: Leaders like Steve Jobs and Elon Musk are known for their transformational approach, inspiring their teams to achieve extraordinary results.
3.2. When to Use
Action: Use transformational leadership when aiming to drive significant change, inspire high performance, or lead innovation.
Benefits: Fosters a positive organizational culture and encourages employees to be proactive and visionary.
Example: Companies undergoing significant change or pursuing ambitious goals often benefit from transformational leadership.
4. Transactional Leadership
4.1. Characteristics
Action: Transactional leaders focus on routine, established procedures, and reward-based performance.
Benefits: This style is effective in achieving specific goals and maintaining organizational stability through clear structures and rewards.
Example: Transactional leadership is often used in environments with well-defined processes, such as manufacturing or customer service.
4.2. When to Use
Action: Apply transactional leadership when the focus is on achieving short-term goals, maintaining order, and managing performance through rewards and penalties.
Benefits: Ensures clarity and consistency in achieving predefined objectives.
Example: Sales teams may benefit from transactional leadership through performance-based incentives and clear targets.
5. Laissez-Faire Leadership
5.1. Characteristics
Action: Laissez-faire leaders take a hands-off approach, allowing team members to make decisions and manage their work with minimal interference.
Benefits: This style promotes autonomy and encourages employees to take ownership of their tasks and projects.
Example: Laissez-faire leadership can be effective in creative or research-based fields where employees are highly skilled and self-motivated.
5.2. When to Use
Action: Use laissez-faire leadership when dealing with highly skilled and experienced teams who thrive on autonomy and self-direction.
Benefits: Encourages innovation and individual initiative by giving team members the freedom to explore and implement their ideas.
Example: Research scientists or creative professionals often excel under a laissez-faire leadership style due to their expertise and self-direction.
6. Servant Leadership
6.1. Characteristics
Action: Servant leaders prioritize the needs and development of their team members, aiming to serve rather than be served.
Benefits: This style builds strong relationships, enhances employee satisfaction, and promotes a collaborative and supportive work environment.
Example: Leaders like Herb Kelleher of Southwest Airlines are known for their servant leadership approach, focusing on employee well-being and empowerment.
6.2. When to Use
Action: Apply servant leadership when fostering a supportive and inclusive culture is essential, and when employee development is a priority.
Benefits: Enhances team cohesion, loyalty, and overall satisfaction by prioritizing the needs and growth of team members.
Example: Non-profit organizations and community-focused businesses often benefit from servant leadership to build trust and support.
Conclusion
Selecting the right leadership style depends on various factors, including your organization’s goals, culture, and the specific challenges you face. By understanding the characteristics, benefits, and ideal contexts for each leadership style, you can choose the one that aligns best with your organization’s needs. Whether you opt for autocratic, democratic, transformational, transactional, laissez-faire, or servant leadership, the key is to adapt your approach to foster a productive, engaged, and successful team.
