SWOT analysis is a powerful tool used in strategic planning to identify and evaluate an organization’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. By systematically assessing these four elements, organizations can develop strategies that leverage their strengths, address their weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats. This article explores the components of SWOT analysis, its benefits, and how to effectively use it for planning.
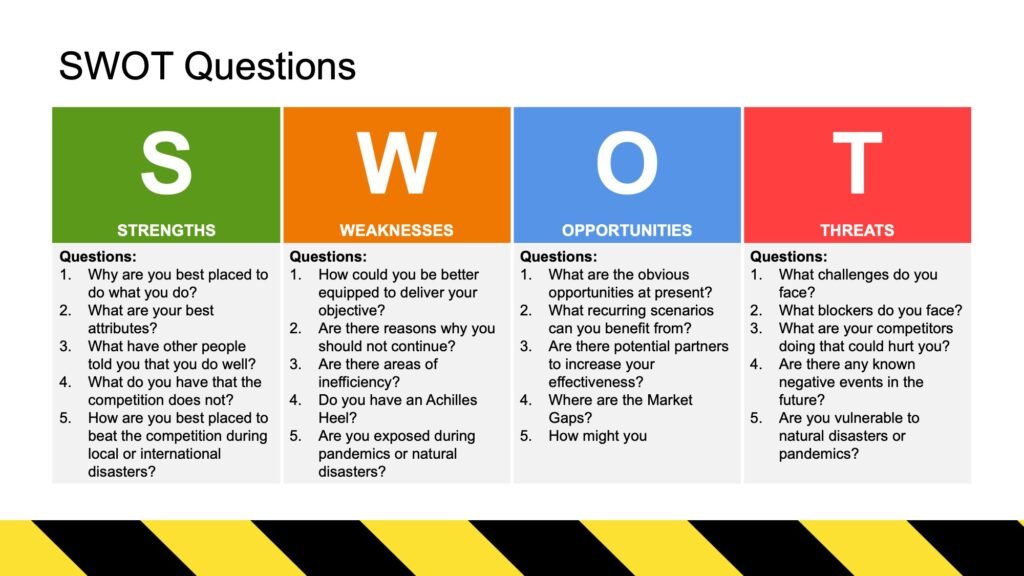
1. Understanding SWOT Analysis
Strengths: Internal attributes and resources that provide an advantage over competitors. These are aspects that an organization excels in and can leverage to achieve its goals.
Weaknesses: Internal factors that place the organization at a disadvantage. These are areas where the organization may struggle or lack capabilities compared to competitors.
Opportunities: External factors that the organization can exploit to its advantage. These are trends, market dynamics, or changes that could benefit the organization.
Threats: External challenges or obstacles that could cause trouble for the organization. These are factors that could potentially hinder progress or impact success.
2. Benefits of SWOT Analysis
Holistic View: Provides a comprehensive understanding of internal and external factors affecting the organization.
Strategic Alignment: Helps align strategies with organizational strengths and opportunities while addressing weaknesses and threats.
Informed Decision-Making: Supports data-driven decision-making by offering a clear picture of the current situation and potential impacts.
Prioritization: Assists in prioritizing strategic actions based on the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
3. Steps to Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Step 1: Gather Information
Description: Collect relevant data and insights about the organization and its environment. This includes internal performance metrics, market research, and competitive analysis.
How to Achieve:
- Internal Data: Review performance reports, financial statements, and operational metrics.
- External Data: Conduct market research, analyze industry trends, and assess competitor performance.
Step 2: Identify Strengths
Description: Determine the internal strengths that provide a competitive advantage. These may include unique resources, capabilities, or positive attributes.
How to Achieve:
- Assess Resources: Evaluate key assets such as skilled personnel, technology, or financial stability.
- Evaluate Performance: Identify areas where the organization performs exceptionally well compared to competitors.
Step 3: Identify Weaknesses
Description: Recognize internal weaknesses that may hinder performance or put the organization at a disadvantage.
How to Achieve:
- Analyze Shortcomings: Assess areas where the organization struggles or lacks capabilities.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from employees, customers, and stakeholders to identify areas of improvement.
Step 4: Identify Opportunities
Description: Explore external opportunities that the organization can capitalize on to achieve growth and success.
How to Achieve:
- Market Trends: Identify emerging trends, new technologies, or changes in consumer behavior that could benefit the organization.
- Competitive Gaps: Look for gaps in the market that the organization can fill.
Step 5: Identify Threats
Description: Identify external threats that could negatively impact the organization’s performance.
How to Achieve:
- Monitor Competitors: Keep track of competitor activities and market dynamics that could pose risks.
- Assess External Factors: Consider economic conditions, regulatory changes, and other external factors that could affect the organization.
Step 6: Analyze and Prioritize
Description: Analyze the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to develop actionable strategies.
How to Achieve:
- Develop Strategies: Create strategies that leverage strengths, address weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and mitigate threats.
- Prioritize Actions: Focus on high-impact actions that align with organizational goals and priorities.
4. Examples of SWOT Analysis
Example 1: Technology Company
Strengths:
- Strong R&D capabilities.
- Established brand reputation.
Weaknesses:
- High operational costs.
- Limited market reach.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand for innovative tech solutions.
- Expansion into emerging markets.
Threats:
- Rapid technological changes.
- Intense competition from industry leaders.
Example 2: Retail Chain
Strengths:
- Wide range of product offerings.
- Strong supply chain network.
Weaknesses:
- Outdated store layouts.
- Limited online presence.
Opportunities:
- Increasing e-commerce growth.
- Expanding consumer base in new regions.
Threats:
- Economic downturn affecting consumer spending.
- Rising costs of goods and services.
5. Common Pitfalls in SWOT Analysis
Pitfall 1: Lack of Objectivity
Description: SWOT analysis can be skewed by personal biases or overly optimistic views.
Impact:
- Skewed Results: Inaccurate identification of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, or threats.
- Ineffective Strategies: Strategies may not effectively address the real issues.
Solution:
- Seek Diverse Input: Involve a diverse group of stakeholders to provide balanced perspectives.
Pitfall 2: Inadequate Data
Description: Relying on insufficient or outdated data can lead to inaccurate analysis.
Impact:
- Misleading Insights: Incorrect assessment of internal and external factors.
- Poor Decision-Making: Ineffective strategies based on incomplete information.
Solution:
- Update Data Regularly: Ensure that data used in the analysis is current and relevant.
Pitfall 3: Failure to Prioritize
Description: Identifying a broad range of factors without prioritizing them can dilute focus and effectiveness.
Impact:
- Scattered Efforts: Resources may be spread too thin, reducing impact.
- Lack of Focus: Difficulty in developing actionable and focused strategies.
Solution:
- Prioritize Key Factors: Focus on the most significant strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Conclusion
SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for strategic planning, offering insights into an organization’s internal and external environment. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, organizations can develop strategies that align with their goals and enhance their competitive position. Effective use of SWOT analysis involves gathering relevant data, involving diverse perspectives, and prioritizing key factors to ensure informed and actionable strategies.
Meta Description: Discover how to use SWOT analysis for effective strategic planning. Explore key metrics, benefits, and steps to align strategy with your organization’s vision.